The loss of baby teeth is an important event for the child and parents. It would seem that not long ago you were waiting for the first tiny tooth, and now it will be in the collection of "mom's treasures," and the permanent tooth will take the vacant place. Caring parents, of course, worried about the question: is everything in order, whether the right change of bite? Let's look into it.
It is impossible to predict exactly when the first baby tooth will fall out - it is very individual. Usually by the age of 5-6 years, the milk roots gradually dissolve, and the tooth, left without a firm hold, falls out easily and painlessly. In just a few days the tip of the permanent tooth shows up. The process of loss of baby teeth takes a few years and is usually complete by the age of 14.
What points you should pay attention to
- It is important to keep your baby teeth until your bite changes. Therefore, oral health should be monitored from an early age. If a baby tooth falls out early, the neighboring teeth will start to shift and there will be no room for a permanent tooth, which can cause the development of bite abnormalities.
- If a baby tooth has fallen out too early, before the age of 5, for some unknown reason, you should see a doctor right away. The specialist will identify factors that may have contributed to the early tooth loss and help avoid bite problems.
- Baby teeth are a guide for permanent teeth. They "show" them where to grow and keep their place. If it is not possible to save a baby tooth before its natural loss, a special construction, a place holder, is put in place.
- By the age of 5, the jaws begin to grow and prepare actively for tooth replacement, and gaps begin to appear between the baby teeth because the size of the teeth themselves do not change. This is done to make room for the larger permanent teeth. If the gaps between the teeth remain unchanged, see your orthodontist to avoid tightness and crowding of the child's teeth.
- It is worth making an appointment to see your dentist if there is a delay in the loss of your baby teeth. There may be different reasons: for example, the milk roots have not resorbed or there are no rudiments of a permanent tooth. Only the doctor can diagnose and solve the problem.
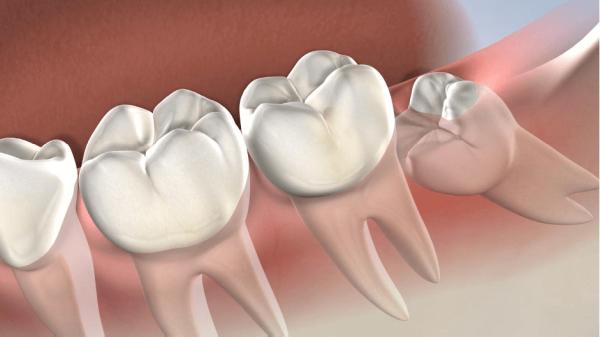
In a normal bite change, two processes occur at the same time: the loss of milk teeth and the eruption of permanent teeth. In this case, the number is different: 28 permanent teeth grow instead of 20 temporary ones. For the eight new chewing teeth there is space due to the expansion of the jaws. The four wisdom teeth, on the other hand, most often erupt in adulthood or may not emerge at all.
Children's teeth fall out in the same sequence in which they appeared: first the incisors, then the chewing teeth, and only after that the canines.
What to do if a baby tooth has fallen out
Normally, the loss of baby teeth is a physiological process and there is little need to interfere with it. If a tooth has been loose for a very long time and is not falling out, causing pain or discomfort, see a pediatric dentist or surgeon.
If a tooth loss occurs at home, there are simple rules to follow:
- Calm your baby down. To keep your baby from fear and stress, turn the loss of a baby tooth into a small ritual.
- Stop the bleeding. You need to press a sterile swab to the gum and ask your baby to bite on it. Usually 10-15 minutes is enough for the bleeding to stop. If it continues to bleed, you need to see a doctor.
- Temporarily limit food intake. After a tooth loss, do not drink for one hour and do not eat for two hours. Give your child only warm drinks and food for the next few days, avoid too cold, hot and spicy food.