Causes of development of reparantitis
Complications can cause any surgical interventions, and implantation is no exception. Most often, the reasons for the reimplant are:
- Poor-quality oral hygiene - leads to cluster pathogenic microflora, which provokes the development of inflammation;
- Medical errors - rejection is associated with violation of the rules of antiseptic processing when installing an implant, lack of preliminary diagnosis of patient bone tissues;
- The use of low-quality materials is the use of implants that are made of low-quality alloys or have untreated surfaces.
Symptoms of re-implantation
Immediately after the impairment of the artificial root, the patient should clearly comply with the recommendations of the dentist. He needs to follow his well-mindedness and pay close attention to any changes in the body's work. Special control requires the location of the implant. Any deviations in the process of implant engraft require a visit to the doctor.
The main symptoms of reimplantite:
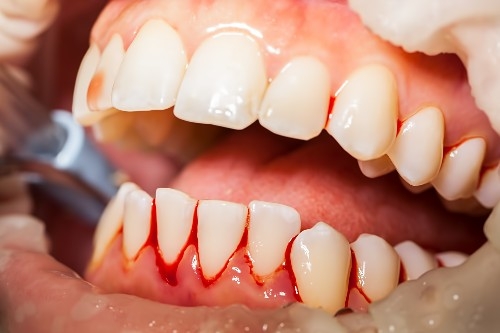
- Swelling, soft tissue hyperemia in the field of implant installation;
- Bleeding gums;
- Pain in the verge of an artificial root that permeate all the jaw;
- The formation of pocket between implant and gums.
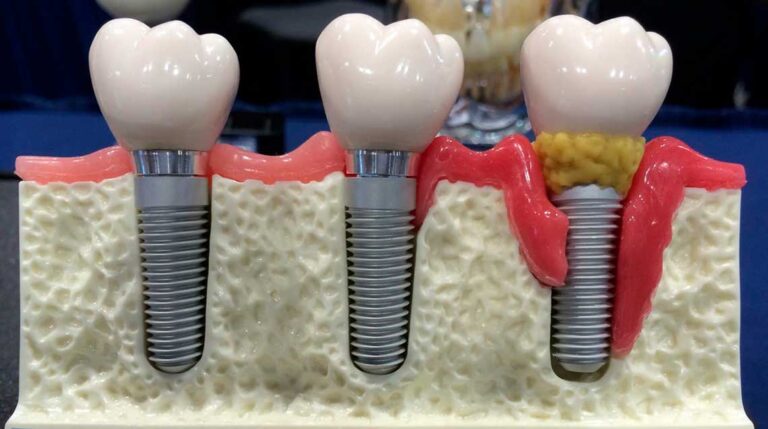
The implant should be resistantly located in bone tissue. If the patient marks at least a little mobility, you need to visit the doctor. Medical assistance will also be required when local suppuration occurs, which indicates the development of inflammation. When visiting the dental office, the doctor will make X-ray portion, and, if necessary, prescribe a dental three-dimensional tomography, which will allow to assess the scale and nature of pathology. To assess the degree of inflammatory process, the dentist takes special samples. As part of the study, the depth of the designer pocket is measured, the degree of mobility of the implant and the nature of the periodontal change is determined.
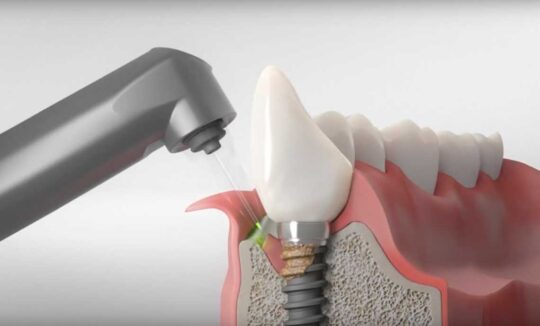
Stages of reparantitis
In the course of its development, the disease passes several stages that have characteristic features:
- Stage 1. The bone tissue is slightly thinned, it becomes like "shy". As a result, accommodation pockets are formed near the implant. There is a redness of the gums, bleeding.
- Stage 2. If you ignore the symptoms of the first stage, inflammatory processes will begin to progress. Soft fabrics become loose, and the gums as it were, "go up" from an artificial root. Gradually occurs the expansion of gums of pockets with the underaction of the inside of the implant. There is a mobility of the implant.
- Stage 3. Strong pain caused by inflammation in the gum appears when contacting with food, toothbrush and other objects. Bone tissue height decreases.
- Stage 4. The last stage is characterized by the complete destruction of Alveolar. The implant actually falls out of bone tissue. At the place of its installation, a fistula with a pus is formed, which brings unbearable pain patient.
Treatment of the disease
Only timely and proper treatment of reimplantite will help warn the rejection of the implant, which was introduced into the human bone. The patient is assigned a comprehensive therapeutic course that includes:
- Medical treatment aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process;
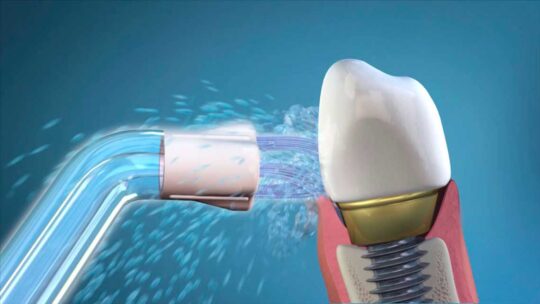
- Ultrasound cleaning;
- Surgical intervention, allowing to eliminate purulent processes and process the surface of implants. Additionally, antibacterial therapy is prescribed with the restoration of bone volume.
Often, bone regeneration and laser and therapy techniques are used in treatment. In order to avoid repeated formation of inflammation after building the bone tissue, an implantoplasty is carried out to the patient. If the disease becomes irreversible, the doctor removes the implant. Next is re-implantation.